Getting Started
This page describes how to install and run bfc.
Installation
Prerequisites
You will need LLVM and Rust installed to compile bfc. For Rust, I recommend using rustup.
LLVM
bfc is built against recent LLVM. See the changelog for information on the most current LLVM version supported.
bfc uses llvm-sys, which wraps the locally installed LLVM.
llvm-sys requires the llvm-config binary to be installed. Check
that your LLVM installation includes this (not all packages do,
especially on Windows).
System LLVM Versions
llvm-sys picks up the default llvm-config binary on your path. If
you want to use a different LLVM version, put it first on your path
and recompile.
$ export PATH="/usr/lib/llvm13/bin/:$PATH"
$ cargo clean
$ cargo build
When testing with different LLVM versions locally, you may find it easier to build with dynamic linking.
$ cargo build --features=llvm-sys/prefer-dynamic
LLVM From Source
You can usually install LLVM from your package manager of choice. Alternatively, you can build LLVM from source as follows:
$ wget http://llvm.org/pre-releases/3.8.0/rc1/llvm-3.8.0rc1.src.tar.xz
$ tar -xf llvm-3.8.0rc1.src.tar.xz
$ mkdir -p ~/tmp/llvm_3_8_build
$ cd ~/tmp/llvm_3_8_build
$ cmake -G Ninja /path/to/untarred/llvm
$ ninja
llvm-sys will use whatever llvm-config is first on PATH. For
example, to use the prebuilt LLVM shown above:
$ export PATH=~/tmp/llvm_3_8_build:$PATH
Compiling bfc
bfc should be compiled with cargo, Rust's packaging and build tool. Cargo will download necessary dependencies (other than LLVM), so an internet connection is required.
$ git clone https://github.com/Wilfred/bfc.git
$ cd bfc
$ cargo build --release
Running bfc
You can now compile and run BF programs as follows:
$ target/release/bfc sample_programs/hello_world.bf
$ ./hello_world
Hello World!
You can use debug builds of bfc, but bfc will run much slower on large
BF programs. This is due to bfc's speculative execution. You can
disable speculative execution by passing --opt=0 or --opt=1 when running bfc.
$ target/debug/bfc --opt=0 sample_programs/hello_world.bf
Cross-compilation
By default, bfc compiles programs to executables that run on the current machine. You can explicitly specify architecture using LLVM target triples:
$ bfc sample_programs/hello_world.bf --target=x86_64-pc-linux-gnu
Diagnostics
bfc can report syntax errors and warnings with relevant line numbers and highlighting.
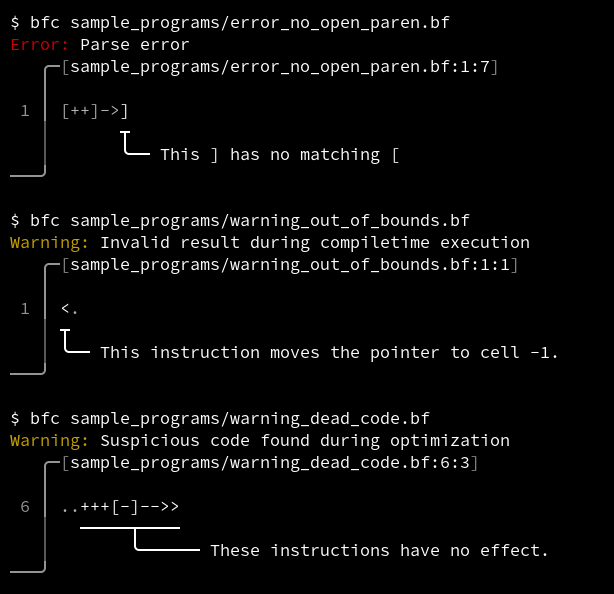
Note that some warnings are generated during analysis for optimisation, so disabling optimisations will produce fewer warnings.